Potential Safety Hazards and Nursing Countermeasures in the Use of Infusion Pumps
- Share
- Issue Time
- Dec 29,2021
Summary
Based on years of experience, BQ+ has compiled the hidden safety hazards and nursing countermeasures in the use of infusion pumps for everyone in this article, so that medical staff can use the infusion pumps correctly.
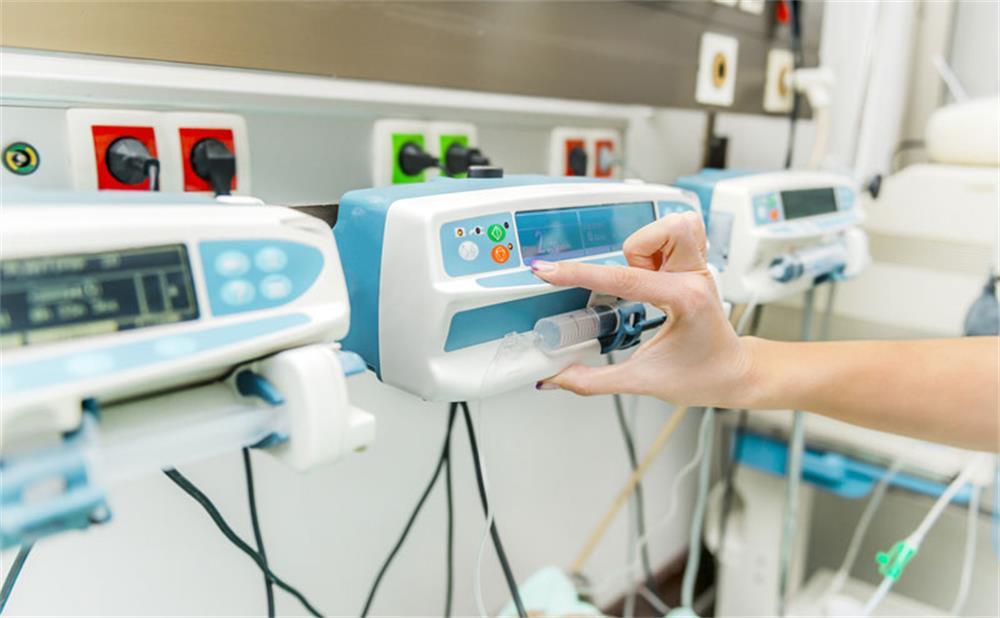

Intravenous infusion is a common treatment method used to achieve the purpose of treatment through intravenous administration. As clinical auxiliary infusion equipment, infusion pumps have been widely used in clinical practice by virtue of the advantages of precise control of the total amount and flow rate of the liquid medicine and reduced nursing workload. Recognition and application. BQ+ has compiled the following safety hazards and nursing countermeasures in the application of these infusion pumps.
Security risks
The opening of consumables leads to abnormal flow rate accuracy of the infusion pump
The infusion pump refers to a precision instrument that can set the total amount of infusion and can control the infusion speed. The working principle of the infusion pump is to control the inflow speed of the liquid through the positive pressure generated by the pump.
Squeeze the infusion tube on the conveyor belt to move the liquid in the tube, and the motor rotates a circle to drive the conveyor to drive it, and output a drop of liquid. The faster the conveyor belt moves, the more liquid is squeezed out, on the contrary, the slower the transmission belt moves, the less the liquid is squeezed out.
Through this design, the speed of the infusion can be accurately controlled. In order to achieve the purpose of safe and accurate delivery of liquid medicine, many functions have been added to the design process of the infusion pump, such as flow rate setting, alarm, bubble detection, drug quantity detection, etc.
The performance of the pump itself and the consumables used to determine the safety of the infusion pump, but many doctors still use the experience of gravity infusion to issue medical orders on the concentration of the drug for infusion using the infusion pump. There is no standardized and unified clinically verified standard.
Due to the changes in the speed and time of the infusion of the drug concentration, sometimes the expected therapeutic effect may not be achieved, and it may also cause some hidden dangers such as phlebitis, venous sclerosis, and contraindications.
Air embolism is prone to occur without a drip-rate detector
In clinical practice, some medical staff is accustomed to counting the flow rate by the number of drops. Theoretically, the volumetric infusion pump can control the infusion rate by counting the number of drops. However, due to the difference in the viscosity of the liquid and the diameter of the pipeline, the size of the liquid is inconsistent, the flow rate of the infusion pump fluctuates, so precision infusion is generally not required for drip counting infusion.
In some countries, it is no longer recommended to use the number of drops to measure the flow rate. Instead, the infusion pump is equipped with a probe clipped to Murphy's tube to detect whether the liquid in the infusion bag is empty.
If the drip rate detector is not used, only the total amount is set. When the liquid is empty, an air alarm will be generated. When the air sensor of the infusion pump fails, it may inject air into the human body; the infusion pump cannot be used extremely thin or extremely thick Otherwise, it will affect the accuracy and affect its alarm function.
If the pipe wall is very thin, it is very easy to cause the bubble alarm to be too sensitive and cause a chaotic alarm. If the tube wall is very thick, the droplets may be adsorbed on the inner tube wall when the drug has strong adhesion to the tube wall, and the air can bypass the side of the droplet and pass through the tube.
The peripheral intravenous infusion pump is prone to infusion extravasation
It mostly occurs in the peripheral veins. Under normal circumstances, if the drug fluid has extravasated to the subcutaneous during the infusion process, as the infusion site swells and the local pressure increases, the fluid infusion speed will slow down or even stop, so use infusion When pumping infusion, the infusion pump will not alarm at the initial stage of exudation but continue to infuse the liquid through positive pressure.
When the pressure in the infusion line reaches a certain limit, the pressure alarm will be issued, and the patient has been infused at this time The site causes serious consequences, leading to skin necrosis and affecting the treatment effect.
Due to vascular hardening, malnutrition, and other reasons, the blood vessels are brittle, the lumen becomes smaller, and the blood flow rate is slowed down. For example, the concentration of intravenous infusion drugs is too high and the speed is too fast, which may aggravate local irritation or even occur extravasation.
Due to technical operations and insufficient assessment of patients, nurses may cause repeated venipuncture, destroying blood vessels, or have a low success rate of puncture or improper needle fixation, which can aggravate mechanical damage and cause drug solution extravasation.
Improper operation leads to an abnormal risk of instantaneous flow rate
Failure to follow the normal operation, such as incorrect or incomplete filling process; use of damaged, weak or unsealed infusion pipelines; loose connections of various components in the infusion route; damage to the collection container components; the internal pressure of the pump is much lower than the surrounding air pressure; the water stop is not closed before the pipeline is released or the water stop is not opened during operation, and the mutual interference of multiple channels will cause instantaneous over-current or no-flow problems.
The medicine does not drip at the beginning of use. The reason is that there is no liquid input for a long time after setting the "Start" button, which can cause venous blood return; the flow rate of the infusion pump is too slow, and the infusion tube is discounted, so that the liquid will accumulate in the extension tube. When the pressure reaches a certain level, the infusion pump starts to alarm and can also cause venous blood return.
If the power socket is not plugged tightly or the storage power supply is exhausted, the input fluid will be interrupted and the venous return blood will be interrupted. If the blood return is handled improperly, the needle will be blocked. For patients with abnormal blood coagulation mechanism, the time from the end of the infusion to the sealing time of more than 1 minute may cause the needle to be blocked, and then there is a risk of thrombosis.
Nursing measures
Use the standard pump pipeline to ensure the accuracy of the flow rate
There are more than 120 kinds of infusion sets for infusion pump consumables. The capacity characteristics, pressure resistance characteristics, and air detection characteristics of each consumable are very different. If the technical characteristics of the infusion pump are ignored and the difference in the characteristics of the consumables is confusing.
The following medical risks: some low-elastic pipelines will quickly fatigue and collapse, and the accuracy will decrease sharply, resulting in abnormal flow rates; high-elastic pipelines will produce a large number of pill metering shocks in the case of blockages; low-density infusion tubing Peristaltic squeezing for a long time will rupture and cause liquid leakage; the exposed liquid of the infusion tube will cause the air alarm to fail.
Application of drip rate detector helps prevent air embolism
In view of the possibility that the liquid droplet is empty, the drip rate detector and the preset total amount should be used to play a double insurance role. In the case of no drip-rate detector, the preset amount of the infusion is preset. The amount must be slightly less than the sum of the amount of infusion and the amount of medicine to avoid emptying of the liquid, and the accuracy of the infusion rate per minute and the amount of the liquid should be evaluated immediately to change the liquid immediately, and targeted prevention can be effectively avoided.
Correctly choose large veins or central veins
Avoid phlebitis and fluid extravasation caused by improper operation, improve venipuncture techniques, and correctly choose vascular applications of vasoactive drugs and high osmotic pressure, irritating drugs. We should choose large veins or central veins.
For patients who use CVC and PICC, flush the tube once every 12 hours to ensure unobstructed. Avoid multiple and long-term infusions at the same site; improve the success rate of venipuncture, avoid multiple punctures at the same site, and properly fix the needle; do not use the maximum bolus pressure for peripheral veins.
When venous blood return is found, different measures should be taken according to the nature of the drug used and the amount of blood returned. For example, insulin, nitroglycerin, and other drugs cannot simply press the fast forward button to process the blood return. If the insulin is too fast, it may cause redness, swelling, itching, and hypoglycemia at the injection site.
The strict and formal operation to effectively prevent abnormal flow rate
The infusion pump in use must ensure the effectiveness of the infusion, dynamically monitor the speed of the infusion and observe whether the infusion is unobstructed, and check whether the connections of each infusion tube are tight to avoid blockage or ineffective liquid input.
Strictly follow the normal operation. When the pump starts to run, the water stop must be turned on; when multiple infusion channels, they should be properly connected, start pump operation, and then open the tee; when stopping the infusion, close the tee first, then stop the pump, and finally Disconnect the connection so as not to cause instantaneous over-current and no-flow phenomenon.
When using infusion pumps, it is necessary to strengthen safety awareness, ensure the normal operation of the infusion pump, improve the use and maintenance of the instrument, and ultimately achieve the purpose of promoting the safe use of the instrument, preventing related accidents, and making the infusion pump a good helper in clinical applications. As an expert who has studied infusion pumps for many years, BQ+ can provide you with some professional guiding opinions.
As a medical product manufacturer with many years of experience, our products are sold all over the world and have received unanimous praise from many customers. Our products have undergone multiple medical certifications, and we also control the quality of our products in all aspects. We are also very concerned about the needs of patients and can provide users with effective solutions. If you want to buy our infusion pump, please contact us immediately!